Web application firewall – WAF – protects the application layer and is specifically designed to analyze each HTTP/S request at the application layer. The OWASP provides a broad technical definition for a WAF as “a security solution on the web application level which – from a technical point of view – does not depend on the application itself.”
Challenges
Enterprises are migrating business-critical functions to web applications in an effort to increase productivity, improve business agility and reduce costs. Furthermore, APIs allow applications to interoperate with other services and save development time. While the migration to web applications provides economic advantages and enables increased business agility, it also creates new security risks and compliance requirements that need to be addressed.
The complexity of attacks and blind spots created due to dispersed networks make traditional solutions obsolete and call for a more robust and comprehensive solution that provides faster protection and reduced maintenance costs. By targeting the application layer, attackers steal sensitive data or exhaust server and application resources using stealth attack techniques that go undetected by traditional security tools. Advanced methods exploit application and API vulnerabilities that present new challenges to web application firewalls (WAFs) in securing an organization.
How can this technology help you?
The web application firewall can be implemented in software, hardware or delivered as a service, running in an appliance device, or in a typical server running a common operating system. It can be a stand-alone device or integrated into other network components.
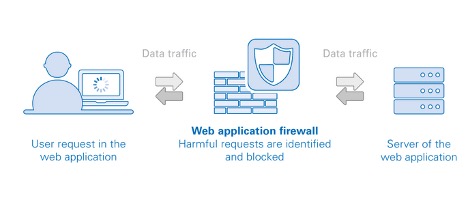
For many organizations, WAFs are a trusted, first line of defense for applications, especially to protect against the OWASP Top 10—the foundational list of the most seen application vulnerabilities.
OWASP Top 10 Web Application Security Risks
Injection
Injection flaws, such as SQL, NoSQL, OS, and LDAP injection, occur when untrusted data is sent to an interpreter as part of a command or query.
Broken Authentication
Application functions related to authentication and session management are often implemented incorrectly, allowing attackers to compromise passwords, keys, or session tokens, or to exploit other implementation flaws to assume other users’ identities temporarily or permanently.
Sensitive Data Exposure
Many web applications and APIs do not properly protect sensitive data, such as financial, healthcare, and PII.
XML External Entities (XXE)
Many older or poorly configured XML processors evaluate external entity references within XML documents.
Broken Access Control
Restrictions on what authenticated users are allowed to do are often not properly enforced.
Security Misconfiguration
Security misconfiguration is the most commonly seen issue. This is commonly a result of insecure default configurations, incomplete or ad hoc configurations, open cloud storage, misconfigured HTTP headers, and verbose error messages containing sensitive information.
Cross-Site Scripting XSS
XSS flaws occur whenever an application includes untrusted data in a new web page without proper validation or escaping, or updates an existing web page with user-supplied data using a browser API that can create HTML or JavaScript.
Insecure Deserialization
Insecure deserialization often leads to remote code execution. Even if deserialization flaws do not result in remote code execution, they can be used to perform attacks, including replay attacks, injection attacks, and privilege escalation attacks.
Using Components with Known Vulnerabilities
Components, such as libraries, frameworks, and other software modules, run with the same privileges as the application.
Insufficient Logging & Monitoring
Insufficient logging and monitoring, coupled with missing or ineffective integration with incident response, allows attackers to further attack systems, maintain persistence, pivot to more systems, and tamper, extract, or destroy data.
Advantages
Web Application Firewall solutions improve the enterprise security capabilities by providing:





